Introducing CSS
- CSS treats each HTML element as if it appears inside its own box and uses rules to indicate how that element should look.
- Rules are made up of selectors (that specify the elements the rule applies to) and declarations (that indicate what these elements should look like).
- Different types of selectors allow you to target your rules at different elements.
- Declarations are made up of two parts: the properties of the element that you want to change, and the values of those properties. For example, the font-family property sets the choice of font, and the value arial specifies Arial as the preferred typeface.
- CSS rules usually appear in a separate document, although they may appear within an HTML page.
Color
- We can specify any color in CSS in one of three ways:
- rgb values: These express colors in terms of how much red, green and blue are used to make it up
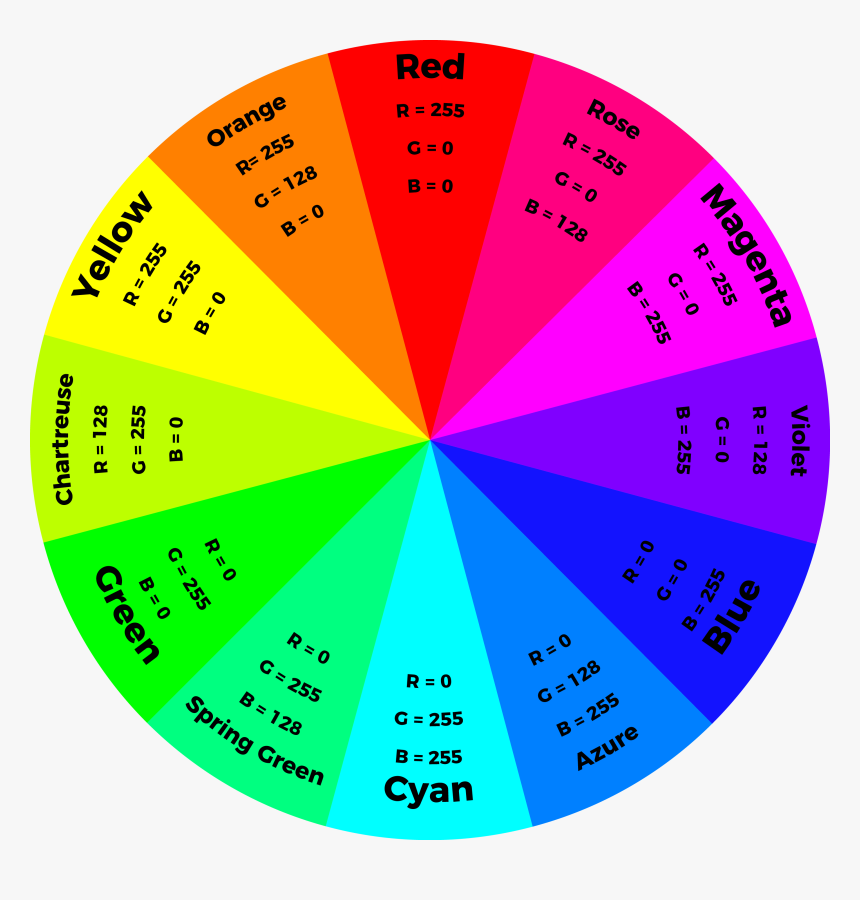
- hex codes: These are six-digit codes that represent the amount of red, green and blue in a color, preceded by a pound or hash # sign.

- color names: There are 147 predefined color names that are recognized by browsers. Like (red, dark blue, gray…etc)

Background Color
we can change the background color of any HTML element, tag or specific part using the <div> tag

Understanding Color
There are many terms that are usful to understand when choosing a color as a backgroung, like:
- Every color on a computer screen is created by mixing amounts of red, green, and blue
- Saturation: Saturation refers to the amount of gray in a color.
- Brightness: Brightness (or “value”) refers to how much black is in a color.
- Contrast: When picking foreground and background colors, it is important to ensure that there is enough contrast for the text to be legible.

CSS 3: Opacity
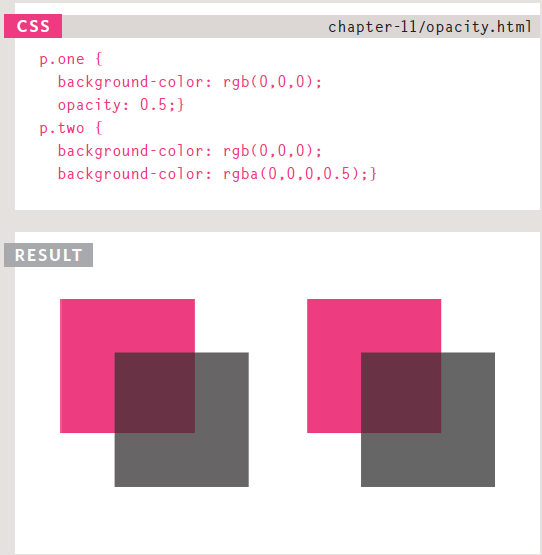
- opacity: CSS3 introduces the opacity property which allows you to specify the opacity of an element and any of its child elements. The value is a number between 0.0 and 1.0 (so a value of 0.5 is 50% opacity and 0.15 is 15% opacity).
- rgba: The CSS3 rgba property allows you to specify a color, just like you would with an RGB value, but adds a fourth value to indicate opacity. This value is known as an alpha value and is a number between 0.0 and 1.0 (so a value of 0.5 is 50% opacity and 0.15 is 15% opacity). The rgba value will only affect the element on which it is applied (not child elements).
CSS3: HSL & HSLA
- HSL stands for Hue,Saturation and lightness. from this we can derive that the hsl system allow the user to determine the previous properties in one line,where H range from 0 to 360, S expressed as a percentage and L also expressed as a percentage.
- HSLA is as HSL** but with the addition of A which stands for *ALpha. Alpha is a property to control transparency just like the opacity property.
